One of the drawbacks of some types of retirement accounts, such as Roth IRAs, is the relatively low contribution limits permitted by the IRS. However, there are tools that can help you save more for retirement while reducing your tax burden in retirement. The mega backdoor Roth is one such tool that may help you increase the amount of tax-free assets you save for retirement.
What is the mega backdoor Roth strategy?
Similar in concept to the backdoor Roth IRA strategy, the mega backdoor Roth (MBD Roth) is a way for those with an employer-sponsored retirement plan (e.g., a 401(k) or 403(b) plan) to potentially save more tax-free funds than the employee elective deferral limits ($24,500 in 2026).
To implement this strategy, you make an after-tax contribution to your employer retirement plan and then convert it to a designated Roth account within the plan or roll it into a Roth IRA. Depending on the terms of your plan, you may be able to contribute up to $47,500 above the 2026 elective deferral limit by pursuing this strategy. It’s important to note that not all plans allow employees to make after-tax contributions, which eliminates the ability to pursue the mega backdoor Roth strategy.
When converted, these funds also gain the other benefits of a Roth account, including no required minimum distributions (RMDs), a tax-free asset for your heirs and potential access to tax- and penalty-free contributions before retirement.
How can I use a mega backdoor Roth strategy?
To use the mega backdoor Roth strategy, your employer plan must allow after-tax contributions and permit at least one of two general ways to execute the MBD Roth: an in-plan Roth conversion and an in-service distribution. Depending on the features of your plan, you may have one, both or neither of these methods available to you. As such, it’s important to review your plan’s Summary Plan Description and talk with your plan administrator, whose contact information is typically on quarterly statements, to determine which options may be available to you.
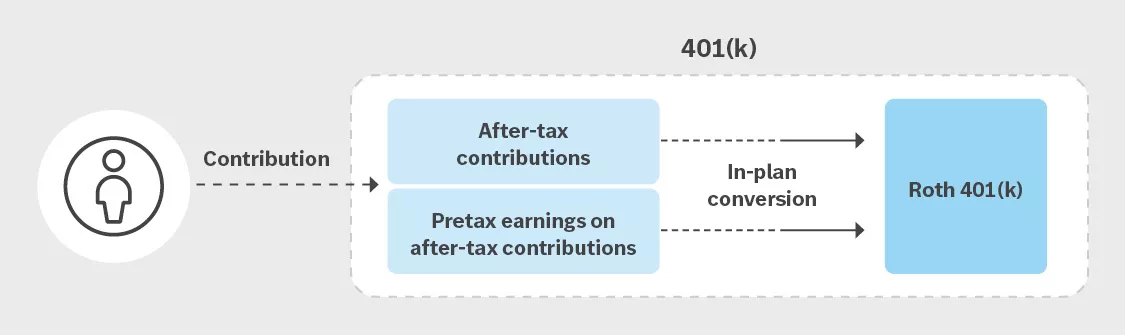
- In-plan Roth conversion: With an in-plan Roth conversion, you convert your after-tax contributions (and any attributable earnings) to a designated Roth account within your employer plan (i.e., a Roth 401(k)). Any earnings converted are taxable in the year you convert them.
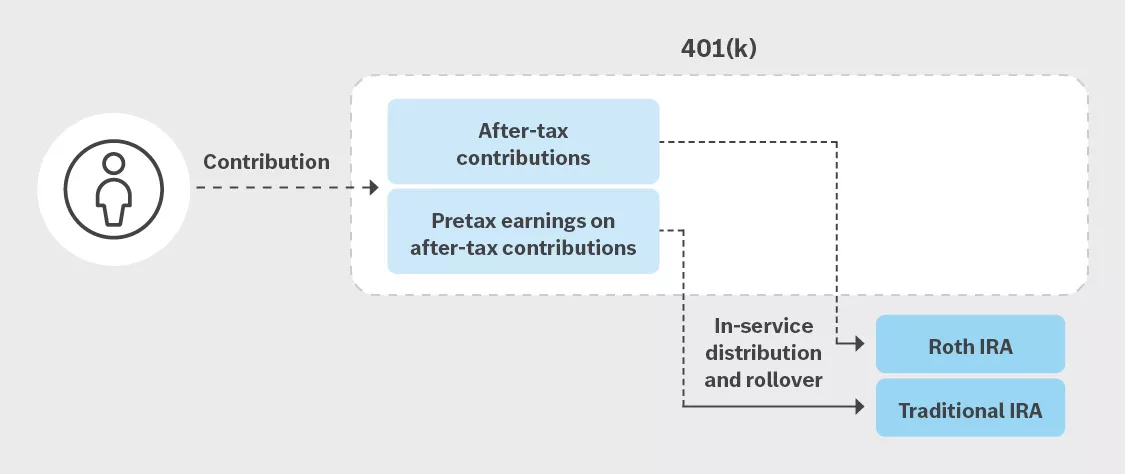
- In-service distribution: An in-service distribution is different because this method moves funds out of your 401(k) and rolls them into your IRA(s). While you can send your entire distribution to your Roth IRA, converting your after-tax contributions to a Roth IRA and sending any pretax amounts to a traditional IRA can be helpful when it comes to managing taxes with your strategy.
How do you manage the taxes with the mega backdoor Roth?
When after-tax funds are converted or distributed from a 401(k), they consist of both after-tax contributions and pretax amounts. This is similar to the pro rata rule for traditional IRAs. Depending on whether your employer separately accounts for your after-tax amounts, the taxable and nontaxable portions of the distribution could be larger or smaller.
As a result, it’s important to talk with your financial advisor and tax professional about ways to manage the taxes with the strategy. Strategies for managing your taxes with the mega backdoor Roth may include the timing of when you roll over or convert the after-tax contributions and separating pretax amounts from the after-tax contributions.
Will the mega backdoor Roth strategy always be available?
There’s no guarantee the mega backdoor Roth strategy will always be available. Congress has considered legislation in the past that would have eliminated this strategy. As of now, the mega backdoor Roth is still around, but no one can predict its future.
The mega backdoor Roth strategy can be beneficial for investors but can easily become very complicated. As such, it’s important to discuss this strategy with your financial advisor to determine if it is right for you and, if so, how to go about implementing it.
Important information:
Edward Jones, its employees and financial advisors cannot provide tax or legal advice. You should consult your attorney or qualified tax advisor regarding your situation. This content is intended as educational only and should not be interpreted as specific investment advice. Investors should make investment decisions based on their unique goals and financial situation. Specific questions should be referred to a qualified tax professional.